With technological and economic developments, India is rapidly approaching its goal of being the world’s most populated nation. The country’s current population density is roughly 428 persons per square kilometre, with a 0.95% growth rate. According to United Nations projections, India will outnumber China in population by 2027. The nation will add roughly 273 million people by 2050, with a current birth rate of 17.163 births per 1000 people.
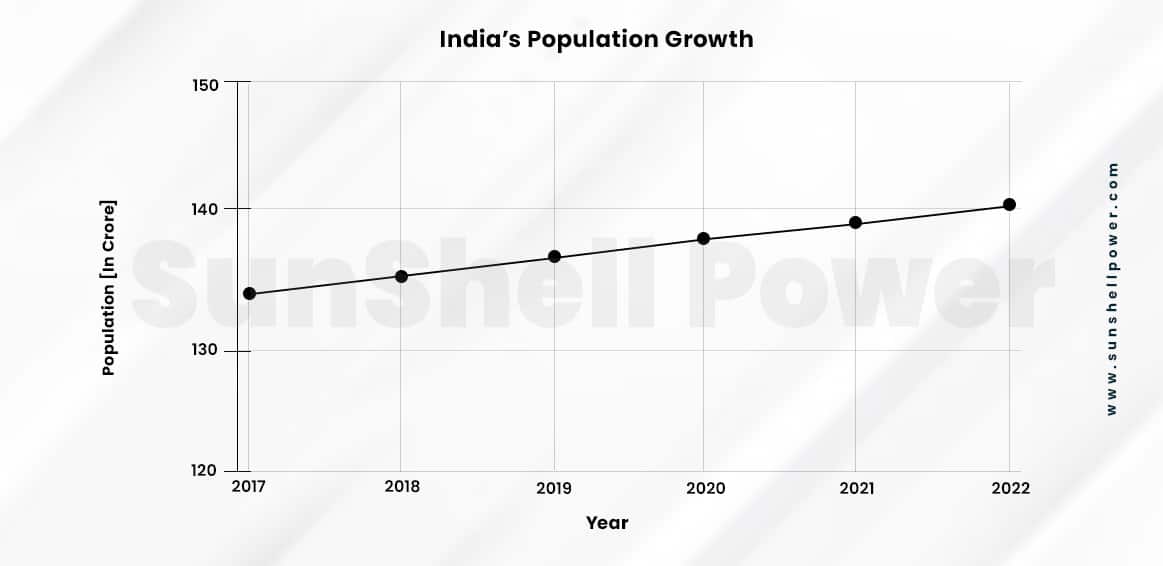
This enormous population growth in India is not only focused on a particular region or specific zone of facility. The population density in every part of the country is equally growing at a rapid speed. Therefore, the accommodation of this increasing population is majorly becoming an issue. In India, the estimated housing shortage is currently around 73.6 million units of which 26.3 million are in urban areas.
As a result, the construction industry in India is expected to grow steadily over the next 4/5 years. The growth momentum is expected to continue over the forecast period, recording a CAGR of 9.5% during 2022-2026.
Even while the business has some severe challenges, such as numerous residential buildings and complexes being vacant at this time of great need, it is mostly the financial component of the industry that is holding it back. The high initial and upkeep costs have prevented poor Indians from owning houses in these residential zones.
The government launched a master plan for multi-modal connectivity in October 2021, with the goal of developing infrastructure to reduce logistic costs and strengthen the economy. As per the investment and recent approaches of the government, the Indian construction industry will reach approximately 1.4 Trillion Dollars by 2025.
Components
Based on waste management, water usage, energy savings, improved ventilation, and rainwater harvesting, residential buildings are graded on these aspects of the buildings. Indian Green Building Council (IGBC) has introduced a rating system to rank residential buildings. The green concepts and techniques in the building sector can help address national issues like water efficiency, energy efficiency, reduction in fossil fuel use in commuting and handling of consumer waste.
According to the Bureau of Indian Standards, the compound and building lighting of a residential building must follow the following rules.
- One-tenth of the floor area for hot-dry climate,
- One-sixth of the floor area for warm-humid climate,
- One-eighth of the floor area for temperature and composite climate,
- One-twelfth of the floor area for cold climate.
According to the Bureau of Indian Standards, solar photovoltaic power plants must be installed on construction plots that are 500 square meters or larger for residential structures. Lighting and other uses inside the home and complex should be made of the electricity produced by the solar plants. These are the guidelines:

Normally a full-size residential complex shall contain these following services based on the size, occupancy and the price of land in the complex: lifts, gyms, compound lighting, building lighting, conference hall, gathering area etc.
Electrical Load
The electrical load of a residential complex depends on various attributes like the size of the complex, no. of residents in the society, size, lighting and electrical appliances of the complex.
Studies show that around 15 watts of power are required for 1sq. Ft area in domestic buildings in normal conditions.
The basic load calculation for a residential complex with facilities like compound lighting, elevator, common area lighting, lift pressurization and the gym is following:
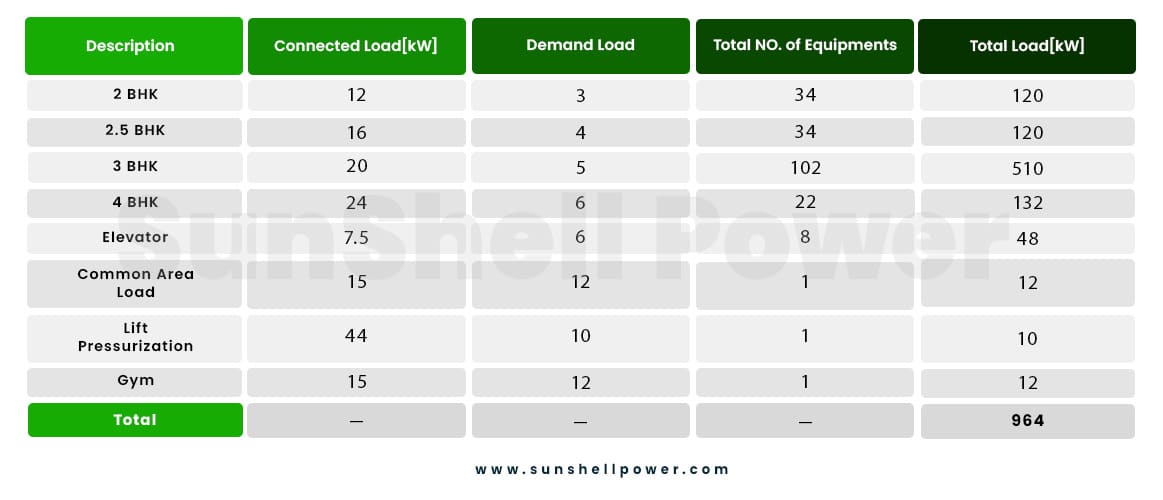
The average annual consumption of residential complexes is around 34.9 kWh per square metre, despite recent awareness initiatives having lowered this figure by roughly 40 to 50 %. However, using energy-efficient goods has greatly decreased overall energy use.
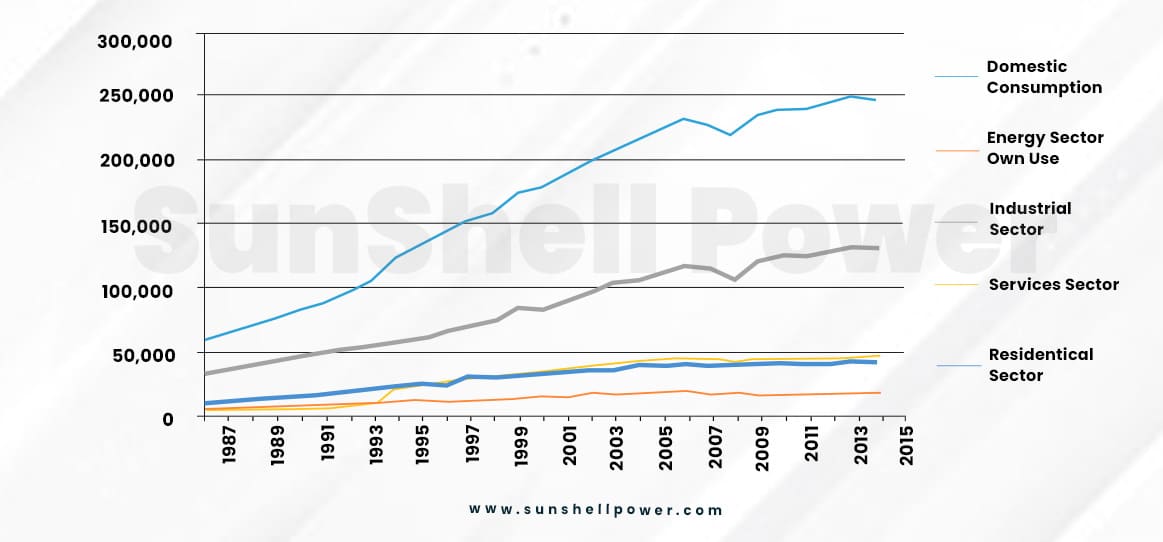
Problems
The decade-long population rise in the country, has affected the accommodation sector of the country, the most. Even though to cater this problem, the residential builders in India, have established a huge number of buildings, the electrical requirements of these houses has caused a lot of problems.
- Huge Energy Gap: India’s third-largest power user, the residential construction industry uses more than 25% of the nation’s total electricity. Between 2014 and 2021, the sector’s average power usage climbed by more than 32%. Despite the fact that the Indian government has implemented a star-labelling scheme for residential structures that is applicable to all single and multiple-family homes used for habitation in the nation. The Energy Star Labeling for old buildings shows a significant EPI (Energy Performance Index) disparity.
There is a big energy deficit in the industry as a result of recent energy disruptions and coal shortages. As a consequence, frequent blackouts have become the norm, making it difficult for the locals to go about their everyday lives.
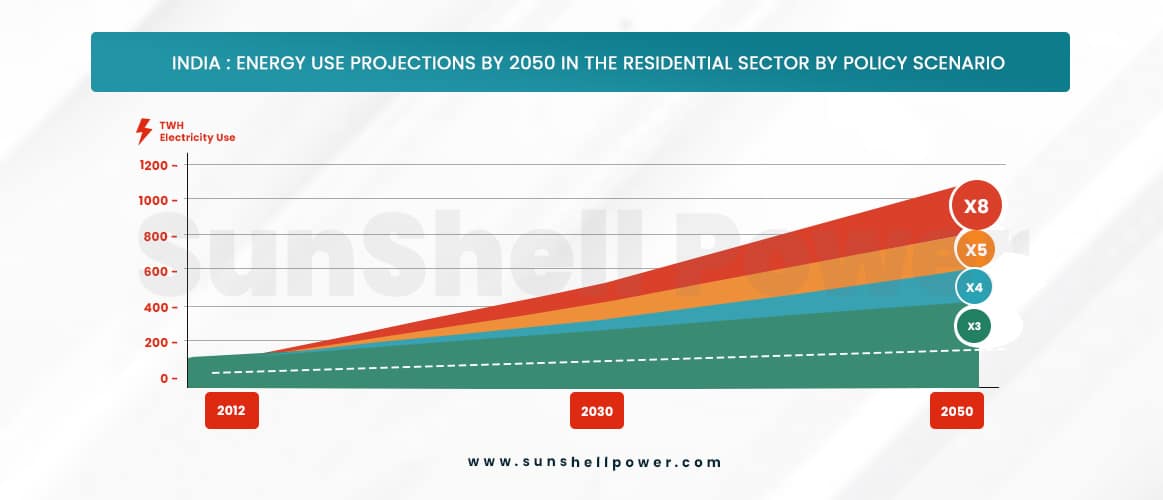
- Carbon Footprint: On April 26, India saw its highest-ever peak electricity demand of 201 GW. Currently, coal makes up over 70% of India’s electricity source, and buildings unintentionally produce a significant amount of greenhouse emissions. In India, the residential sector accounts for just 4% of total emissions, whereas the building industry alone is responsible for 22% of them. Even though India’s overall carbon emission in 2021 was 2.88 GT, and the reduction in the carbon footprint from 9.6% to 4% has been significant. As a result, 4% of this enormous amount is a significant sum.
Even though the carbon footprint has been reduced drastically from 9.6% to 4%, keeping in mind that India’s total carbon emission in the year 2021 was 2.88 GT, the 4% of this huge quantity is a huge amount. - Usage of Excess DG Motor: Recent power outages in Summer 2020, April 2022, etc. have forced buildings to employ diesel generators to provide the homes with the required power supply. For every litre of fuel used, a diesel generator typically releases 2.62 kg of CO2. Therefore, in order to power a 1 square metre area, around 28 kilogrammes of carbon dioxide must be released into the atmosphere each day. In order to recycle that much carbon dioxide, about 2 trees must be planted each day. Using diesel generators excessively raises the building’s operational costs in addition to producing carbon emissions.
- Higher Tariff Charges: The big residential consumers draw a lot of power from the grid providers. As the tariff charges are rising day by day, the energy cost also rises accordingly.
So, What’s The Way Out? Solar Solutions for Green Building
With the development of technology, human society is moving more and more toward renewable energy. The most reliable renewable energy source is solar electricity. For every solar-powered residential society, SunShell Power offers a solar rooftop option. The plant’s solar modules have a 25-year life expectancy and need minimal maintenance, making it a reliable source of energy.
For solar green building, we offer two types of solar solutions:
- Grid-connected Solar Rooftop Plant
- Solar Street Light
Grid-Connected Solar Rooftop Plant(On-Grid):
Grid-connected solar rooftop power plant with little maintenance and accessible net-metering capability, as well as a credit system based on power banking. This sort of power plant is excellent for establishments with high demand and infrequent power outages.

Why On-Grid?
Now, the question may arise to your mind- “Why should I invest in solar?”
Solar power plants are a terrific financial and economical investment that is unquestionably a dependable source of electricity, in addition of being environmentally beneficial and producing green energy.
We’ve compiled a list of eight overall advantages of installing solar rooftop power plants based on feedback from prior customers:
- Reduced electricity costs as dependency on conventional electricity are reduced,
- Reduced bills on running DG generators due to frequent voltage drops,
- The government gives subsidies for solar panel installations,
- Tax benefits by going for accelerated depreciation,
- Easy availability of loans at low-interest rates for solar panel installations,
- Low maintenance and long life span,
- Environment-friendly solar power is the best way to preserve our planet,
- Proper utilization of the unused space on the rooftop,
- By installing rooftop solar power plants, a medium-size residential society can save up to 1 million trees annually,
- Installing the solar plant can save a significant amount of money in roof covering costs. The panels are integrated to be a part of the roof. Solar panels can reduce the roof-surface temperature of a building by up to 38%.
- Solar rooftop power plants can help a residential building achieve green building certification from the Indian Green Building Council.
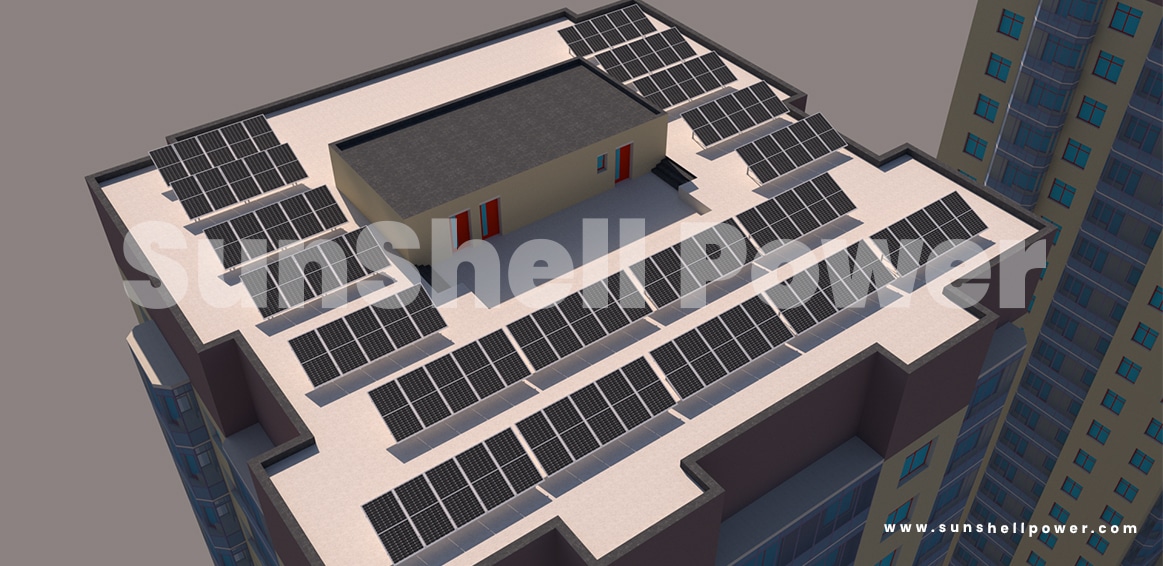

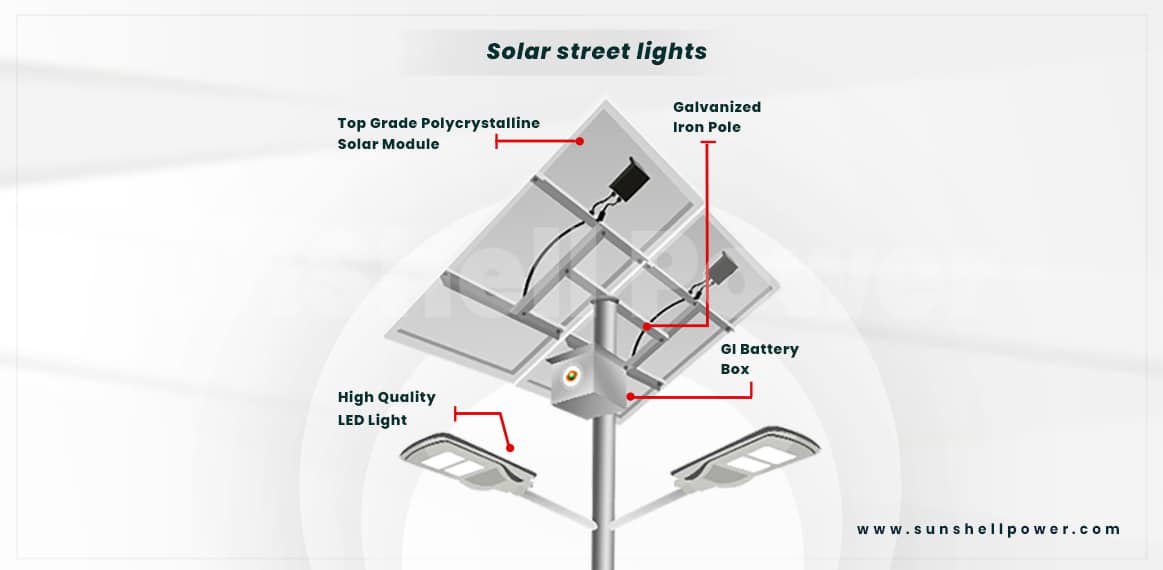
Solar Street Light
Proper compound lighting and illumination are essential requirements for the health and safety of the residents. The Bureau of Indian Standards has also standardized the proper lighting standard for each type of building and residential building as discussed above. Solar street lights are the best option for the purpose. For big complexes, regular street lights tend to increase the electrical cost by a huge amount while solar street lights come with a 5-year warranty and produce proper illumination while generating green energy.
- Two in One (Semi-integrated): Used for a variety of purposes, these are easy to install and are low-maintenance.
- Solar Mini Mast: Best for places with unstable power sources, uses green energy and needs almost zero maintenance.
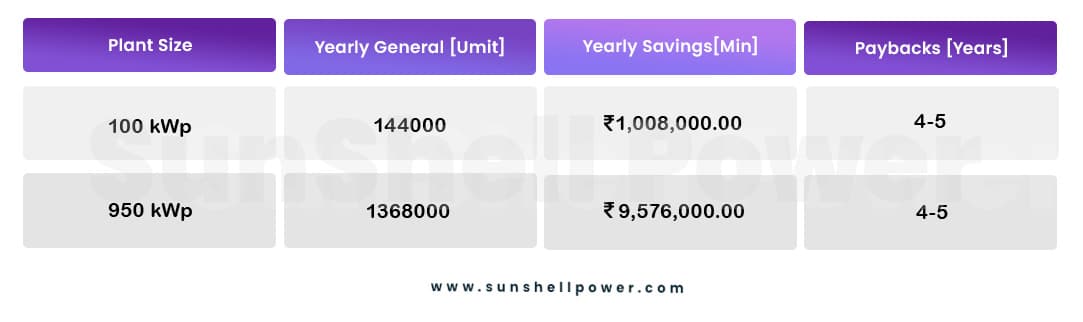
Average ROI:
The average ROI of a grid-connected solar plant in a residential society is around 4-5 years, although it can change based on the load of the health facility.
Become A Part of The Green Future – Solar Solutions for Green Building:
Residential complexes must adapt to the green solar power plants as the globe goes more and more toward green energy and renewable energy sources in order to meet the Central Government of India’s goal of achieving net-zero emissions by the year 2070.
Recently, housing associations from different cities have started installing solar rooftop panels in order to start and register for The Indian Green Building Council’s Green Building Category.
Green buildings can have tremendous benefits, both tangible and intangible. The most tangible benefits are the reduction in water and energy consumption right from day one of occupancy. The energy savings could range from 20-30% and water savings around 30-50%.
The intangible benefits of green new buildings include enhanced air quality, excellent daylighting, health benefits etc.
The intangible benefits of green new buildings include enhanced air quality, excellent daylighting, health benefits etc.
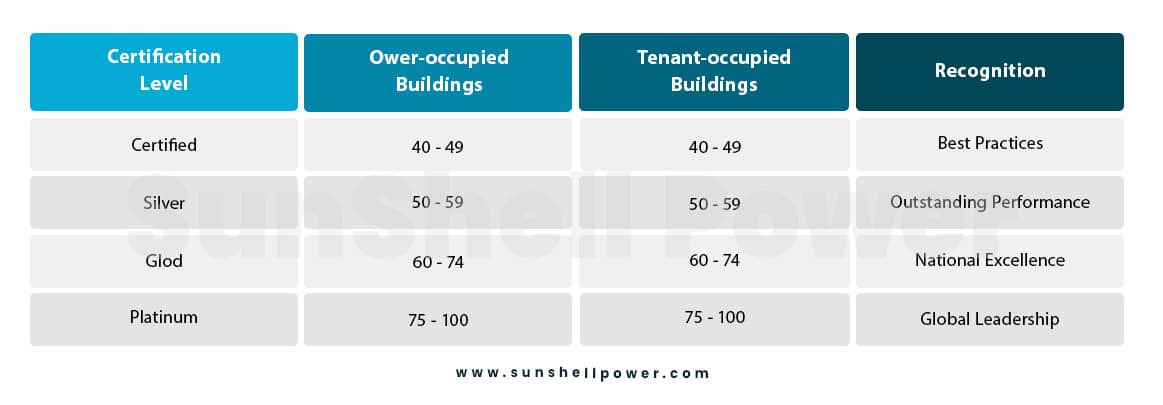
The certification levels of the buildings are the following:

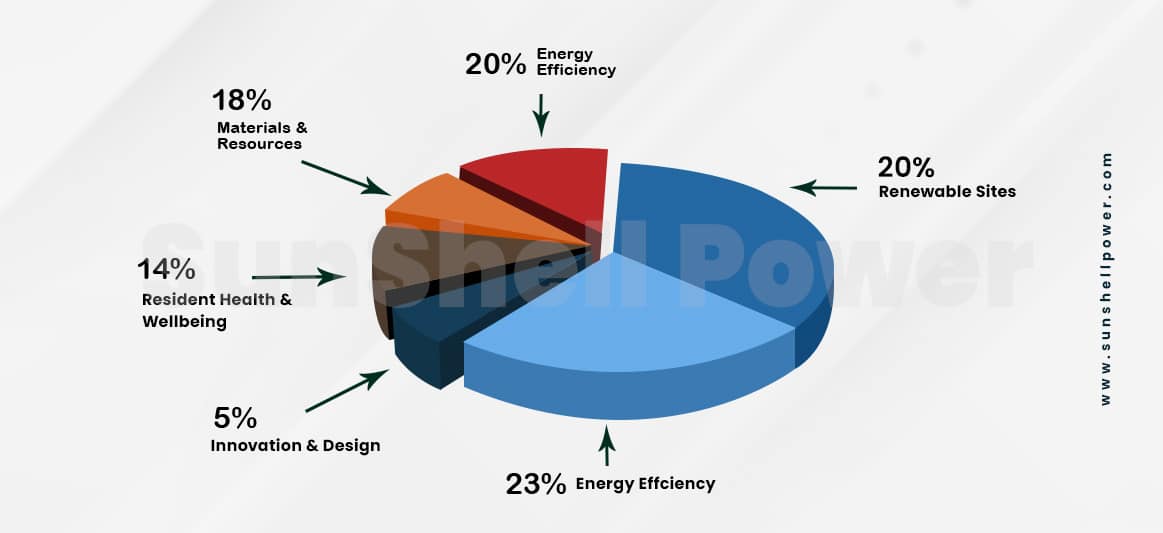
The IGBC Green Homes rating system addresses green features under the following categories:
- Sustainable Sites
- Water Conservation
- Energy Efficiency
- Materials & Resources
- Resident Health & well-being
- Innovation & Design
- Benefits of Green Building: The Indian Green Building Council shows that Green Building is not just a term, there are several benefits of being and recognised as a green building:
- Reduction of natural resource consumption
- Reduction of operating costs
- Health, comfort and safety for all residents
- Energy conversation and consumption optimization
- Increased productivity of the occupants
- Enhanced indoor air quality ( IAQ has a tremendous impact on human health)
- Companies are encouraged by green building to reap the benefits of a green corporate image and make a great first impression on customers, staff, business partners, and shareholders.
In the year 2016, a residential complex in Pune, consisting of 219 apartments installed a 50 kW solar power plant saving approximately Rs. 10.80 lakh during the first year.
There are quite a few examples of successful solar installations in residential complexes, managed by SunShell Power. Some of them are 81kWp On-Grid Rooftop Solar Power Plant in Kolkata, and 189 kWp On-Grid Rooftop Solar Power Plant at Serampore, Hooghly.
Enquire Now

